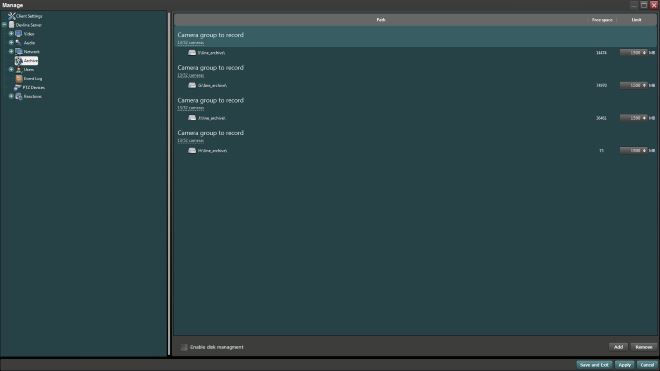
One of the latest innovations of the MyVMS is the ability to assign parallel recording of cameras to different disks.
Click the image to view
The archive engine allows you to:
- organize RAID software (same as RAID 0);
- set the archive depth for different cameras (groups of cameras);
- configure camera recording priority.
It is recommended to assign a maximum of 16 cameras to one physical disc drive with a total recording flow of no more than 250 Mbps. The system allows a setting up where each camera has separate HDD for recording.
The same camera and source of the recording can not be assigned to different groups. The program has the cyclic video recording mode: if the disk space is over the program will start to write new data over the old one. If several folders for archives were assigned for a group, they will be filled sequentially.
HDD parameter selection
While choosing an HDD it is essential to take into consideration the required twenty-four-hour operation. Such operation is one of the key user requirements to surveillance systems. Choose surveillance system hard disks carefully, since they operate under high loads. It doesn't mean that it is necessary to use only highly specialized disks for video recording, it is possible to choose the appropriate hard disk drive following the next parameters:
- 24 х 7. Mode of operation — 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). MTBF parameters for each HDD model can be found on manufacturers' websites. The higher such MTBF parameter is, the longer an HDD works. Generally, the majority of hard disks have appropriate MTBF level but there are exceptions as well, such as Enterprise and server solutions.
- Revolutions Per Minute (RPM). It is one of the key parameters defining the operating speed of hard disk storage. This value is measured in revolutions per minute and is directly related to the linear speed of reading heads. It is not recommended to use HDDs with less than 7200 rpm for comfortable and fast archive processing. If you choose an HDD with high RPM value, give some consideration to the cooling system.
- Random Access Time. This parameter displays the average time a hard disk needs to locate a magnetic head to a random spot of a disk. Range is from 2.5 to 16 ms.
- Input/output operations per second (IOPS). Modern HDDs process about 50 iops for random access and 100 iops for sequential access.
- Hard disk capacity is chosen in terms of archive depth requirements with 5-10% of reserve storage.
- HDD interface. We recommend using SATA Revision 3.0. This version of the Serial ATA interface is fully compatible with the previous ones and has the same types of slots and cables as the SATA-II.
HDD monitoring
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology; often written as SMART) is a monitoring system used on computer hard disk drives that detects and reports on various indicators of drive reliability with the purpose of forecasting hardware failures.
When S.M.A.R.T. data indicates a possible imminent drive failure, the host system software may notify a user to copy stored data to another storage device, preventing data loss, and replace the failing drive.



